Let Us Know How We Can Help. We Are Your Dedicated Solutions Provider.
Why Choosing the Right PCB and Assembly Process is Crucial for Your Project?
Choosing the right PCB and assembly process can make or break your project. In the electronics industry, every detail matters. A well-structured PCB can enhance performance and reliability. However, poor choices can lead to failures, delays, and increased costs. Consider the complexity of modern devices. Each component requires precise placement and connections.
Attention to the assembly process is equally important. The method impacts product durability and efficiency. Using the wrong technique could lead to defects. These defects may not show up until after the product launch. Such outcomes can tarnish a brand's reputation.
Reflecting on past experiences highlights the need for careful planning. Unexpected issues can arise from seemingly minor decisions. Ignoring these details may result in significant setbacks. Prioritizing the right PCB and assembly techniques ensures a smoother path to success. It also positions your project for future growth and innovation.
Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding the Basics of PCB and Assembly Processes
Choosing the right PCB and assembly process is essential. It starts with understanding the basics of these processes. A printed circuit board (PCB) is a backbone for electronic devices. It connects components using conductive pathways. The design phase is critical. Small mistakes can lead to significant failures later.
Assembly processes vary. Some use automated machines, while others rely on manual labor. Each method has its pros and cons. Automated assembly can save time but may miss small defects. Manual assembly allows for quality checks but is slower. It’s essential to assess project needs carefully. An assembly method that works for one project may not suit another.
Errors in choosing materials can also cause issues. Using low-quality components might save money, but they can lead to malfunctions. Every detail matters, from soldering techniques to testing procedures. Each step can impact the project's success. Reflecting on choices made during the design and assembly phases can be crucial for future projects.
PCB Manufacturing Methods and Their Impact on Project Efficiency
This chart illustrates the production time associated with different types of PCBs. Understanding these differences is crucial for determining the most efficient assembly process for your project.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing PCB Materials
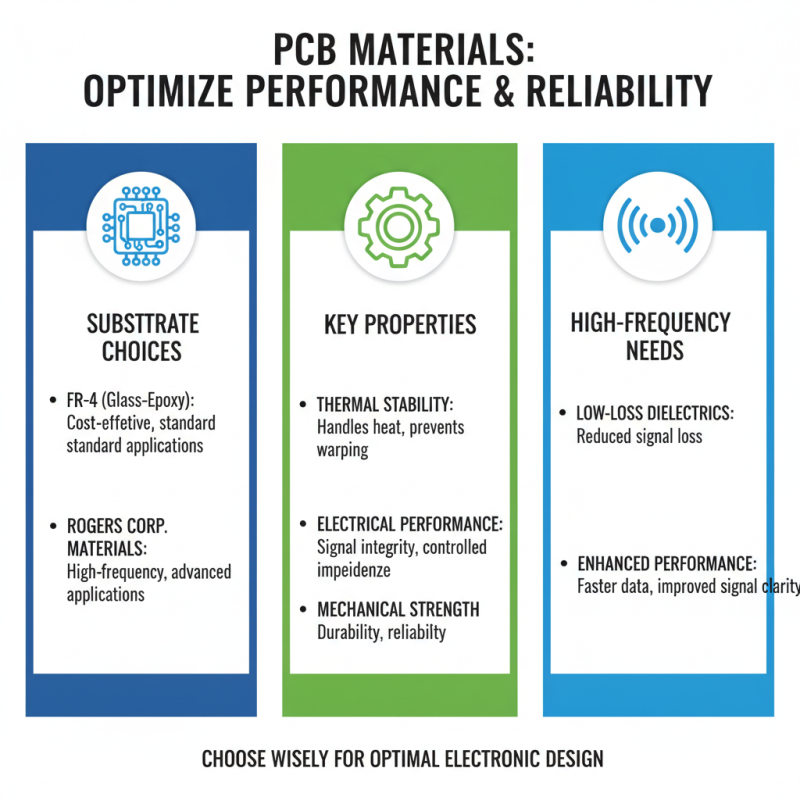
Choosing the right PCB materials is essential for ensuring performance and reliability. The substrate, often made of FR-4 or Rogers, affects signal integrity. Different materials have unique properties, such as thermal stability and electrical performance. For high-frequency applications, using low-loss dielectric materials can significantly enhance performance.
Cost is a major consideration when selecting PCB materials. While higher-quality materials may seem expensive, they can save money in the long run. Poor material choices may lead to failures or rework. It's crucial to weigh the initial costs against potential losses.
Environmental factors also play a significant role. PCBs exposed to high temperatures or humidity may need specialized materials. Using the wrong type can lead to delamination or short circuits. Analyzing the environment where the PCB will operate is fundamental for durability and longevity. Understanding these factors can prevent future issues.
Different Types of PCB Manufacturing Techniques Explained
When diving into PCB manufacturing, understanding different types is essential. Each technique offers unique advantages. For example, traditional subtractive methods involve etching copper from a substrate. It’s a common choice but can produce waste. Proton beam and laser techniques emerge as modern alternatives, providing precision. However, they come with higher costs and require specialized equipment.
Another option is additive manufacturing. It builds circuits layer by layer, reducing material waste. Yet, this process is still evolving. Therefore, the quality and reliability of the final product can be uncertain. In contrast, hybrid processes combine subtractive and additive techniques. This can yield high performance, but it complicates production processes. Attention to detail is vital in this context.
Choosing the right technique should align with project goals. Different products may require different approaches. Assessing design complexity, budget constraints, and production timeline is critical. A poor choice can lead to delays or increased costs. Mistakes in the manufacturing phase often arise due to oversight. Balancing innovation with practicality remains a challenge for many.
The Impact of Assembly Processes on Product Quality and Reliability
When it comes to electronic projects, assembly processes play a critical role in determining product quality. The right assembly method influences how components adhere to the printed circuit board (PCB). For instance, improper soldering can lead to weak connections. This might cause the end product to fail under stress.
Surface-mount technology and through-hole insertion each have their advantages. Surface-mount technology allows for compact designs, but it can complicate repairs. On the other hand, through-hole is typically more robust. However, it takes up more space. Each choice comes with trade-offs that must be weighed.
Additionally, quality control during assembly is vital. Inadequate inspection can result in defective products reaching consumers. Testing methods vary, but many often overlook critical checks. Such oversights may have long-lasting effects on reliability. Each stage of the assembly process requires careful thought. Without attention to detail, even a small mistake can lead to product failures, affecting the overall success of a project.
Cost Considerations in PCB and Assembly Process Selection
Selecting the right PCB and assembly process involves careful cost considerations. The overall budget for a project heavily influences these choices. A lower-quality PCB might save money initially. However, it can lead to increased failure rates and higher long-term costs. It's critical to evaluate the entire lifecycle cost, not just initial expenses.
Material choice plays a significant role in cost. For example, some materials may be cheaper but lack durability. This can result in frequent revisions and replacements. Assembly techniques also vary in cost and efficacy. Complex processes might provide better performance, but they can significantly increase the bottom line. Sometimes, simpler methods yield satisfactory results.
It's easy to overlook hidden costs. Testing and compliance can add unexpected expenses. Additionally, time delays in production can escalate costs quickly. Reflecting on past projects can provide insights. Were there moments when cutting costs led to regrets? Balancing quality and budget is essential. It's a tricky landscape to navigate.
Related Posts
-
Maximizing Efficiency in PCB Assembly Through Advanced Automation Techniques for 2024
-
Top 10 Tips for Effective Circuit Board Design Strategies?
-
Top 10 Benefits of Circuit Board Assembly for Modern Electronics?
-
Ultimate Guide to PCB Design and Assembly Best Practices for Beginners
-
Exploring the Evolution of PCB Fabrication: From Concept to Reality in Modern Electronics
-

The Future of Electronics: How PCB and Assembly Technology is Shaping Tomorrow's Devices
